Survival, recovery, and building resilience: Transformation of financial institutions in the times of COVID-19 – Part 2
 by Anup Singh and Graham Wright
by Anup Singh and Graham Wright Aug 21, 2020
Aug 21, 2020 7 min
7 min
This blog looks at how financial institutions can build upon the survival strategies to recover and transform during the COVID-19
pandemic and afterward.
In the previous blog, we discussed the impact of COVID-19 on individuals and businesses, much like Philip the fruit seller in Nairobi. The recovery of individuals and businesses depends on the revival of financial institutions. Further, we discussed actionable strategies for financial institutions to survive the crisis. In this blog, we discuss how financial institutions may build upon the survival strategies to recover and transform during the pandemic and afterward.
Different financial institutions will have suffered varying degrees of disruption due to the pandemic. Some might not even survive. They need critical knowledge and financial expertise for adaptive leadership and business continuity.
To recover, financial institutions must revive their portfolio, execute new funding strategies, manage costs, and engage in digital transformation. The recovery phase may anchor on the assessment of key customer segments, including the low- and moderate-income clients and entrepreneurs that the institution. The institutions may set up a responsive structure to help clients recover after the pandemic. Thereafter, the institutions may begin to assess the utility of digital processes and channels. Aligning digital initiatives to the needs of its users will provide an edge to the institution in its recovery. The design of digital initiatives should suit the context where the virus remains a reality. Besides, the institutions may create strong marketing, branding, and communications functions to reach out to customers.
We project that full person-to-person interaction will be feasible not before four to six months, and quite possibly in the months further ahead, subject to careful hygiene protocols. Thus, the digital solutions will need to be built on the understanding of the customers and a humane approach to the customer problems in the current context. A high-tech and human touch model may be enabled through the relationships, data, innate customer awareness, and local understanding.
Based on MSC’s experience with financial institutions, we make the following recommendations for financial institutions to recover and build resilience in the post-COVID-19 phase.
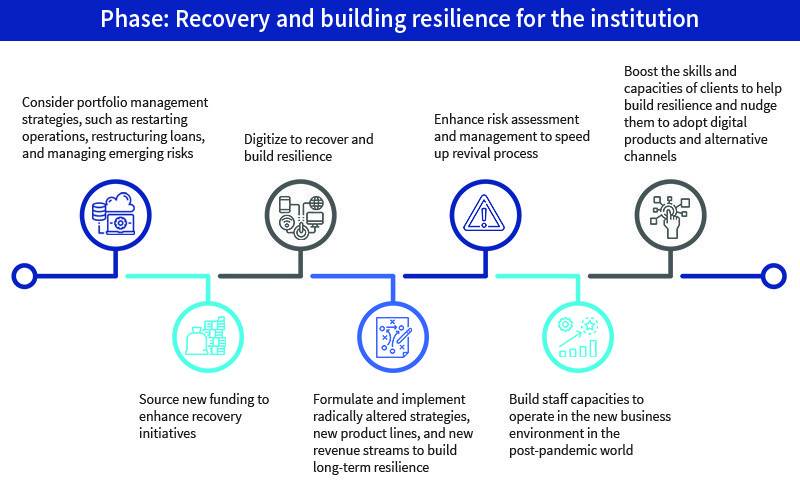
6.Consider portfolio management strategies, such as restarting operations, restructuring loans, and managing emerging risks
In the recovery phase, financial institutions may revive their portfolio by restarting operations in the areas that have either recovered or are less infected. The institutions may devise portfolio planning and management through a mix of segmentation, risk analysis, and stress testing scenarios.
As the businesses/daily lives of the clients are affected due to the pandemic, the institutions may need to restructure and refinance. This will enable clients to use additional credit to recover their businesses. However, the institution may use a segment-wise portfolio analysis to decide on the set of clients to restructure loans. Financial institutions may develop a matrix to score clients and segments to decide appropriate actions. The scoring matrix may consider the impact on the business, finance, workforce, and households; coping strategies; and outlook. Using a simplistic scoring tool, the institutions may prioritize the clients segments to focus upon and action plans.
The institutions may also need to focus on managing risks associated with the recovery phase. Some of the risks to focus upon include financing the operations and business, credit and recovery, and fraud and misrepresentation.
7.Source new funding to enhance recovery initiatives
As financial institutions build recovery strategies, they will need to execute new funding strategies. To do so, they will need to reposition the institution as they rebuild after the pandemic. They will also have to understand the current priorities of donors and investors. The financial institutions may identify the funding opportunities to assist the recovery efforts. The institutions may also identify the key government support programs for the financial sector. Thus, financial institutions may raise funds for the recovery phase by utilizing government programs, donors, and investor responses.
8.Digitize to recover and build resilience
As the period of the pandemic and after is and will be characterized by digital engagement, financial institutions may assess the digital inclusion infrastructure and environment and determine opportunities in the market for financial institutions. Financial institutions may recover and build long-term resilience through digital transformation.
The first step to digital transformation for any financial institution is the assessment of its digital transformation readiness. An ideal digital transformation readiness assessment may include the following elements:
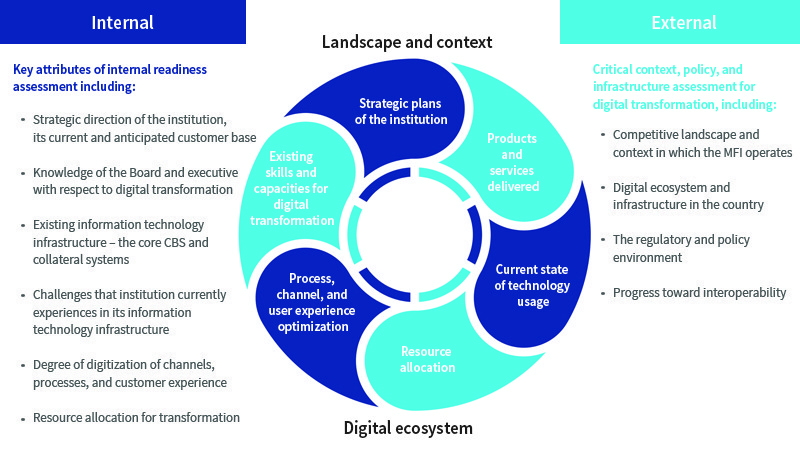
Digital transformation for organizations is about offering the right combination of 1) digital solutions or tools, 2) delivered digitally, 3) riding on digital technology, 4) that provide a seamless user experience. Digital transformation for financial institutions may include:
- Business model and products: Digitization fosters innovation across the business model and products
- Processes: Automation of repetitive, low-value, and low-risk processes; digitization helps in enhancing the efficiency and managing risks for the back-end and front-end processes
- Channels: Digitization of the traditional channels
- Engagement and user experience: Enhanced engagement with customers, employees, and suppliers; use of technology to offer superior user experience
Financial institutions should use the crisis as an opportunity to digitize their business model and operations. We have seen that a growing number of financial institutions are now gearing up their digital transformation efforts and will quickly eat into the markets of analog financial institutions.
During the pandemic and after, financial institutions may use digital transformation to:
- Use digital channels to optimize loan disbursement and repayment
- Increase digital client engagement through client relationship management

- Build or revise the existing digital credit-scoring module for existing and new clients
- Develop digital staff engagement workflows and integrate into the human resource management plan
- Digitize client engagement through tablets that can capture biometrics and other loan application requirements
- Create an electronic data management system to manage client-related data and to run advanced analytics
- Digitize internal business processes to optimize costs and increase efficiency
- Utilize digitization to engage with new and existing clients
- Re-orient staff to digitization; this may include new business processes and new business tools anchored on technology
- Revamp the client relations management system to include regular client engagement messages. Text message blasts, interactive video responses, and comics to deliver to clients
The digital transformation strategy for each financial institution needs to be customized and contextualized. The financial institution may need to develop unique, individual, and customized digital solutions that build on the current limitations of using physical touchpoints as is the case now.
9.Formulate and implement radically altered strategies, new product lines, and new revenue streams to build long-term resilience
In the next phase, the institutions will need to transform radically to build resilience based on the level of preparedness, macro-economic conditions the financial institution operates in, and the context.
As part of the revival and resilience-building efforts, institutions may develop new product mixes, such as new credit lines and innovative savings initiatives geared to insulate clients against future disasters. Further, institutions may build partnerships to offer products like wholesale lending credit lines for businesses to revive.
The institutions may assess and focus on serving the top-performing client segment post-pandemic. Through constant market intelligence, the institutions may develop a list of top-performing sectors. These sectors will have businesses and activities that have faced minimal disruption and risks due to the ongoing pandemic. Besides, institutions may develop or strengthen partnerships in the delivery of financial services. They may need to identify new opportunities, such as that of money transfer and payments to tap into a new market. They may also explore new revenue streams, such as disbursement of government benefits to the low- and moderate-income populations.
10.Enhance risk assessment and management to speed up the revival process
The institutions will need to enhance the risk management approaches significantly, especially for their credit portfolio. They can do so by identifying the existing and new risks, assessing the nature of risks, and validating the existing risk management framework. They may need to re-calibrate the indicators and triggers of all risks in line with shocks and impact on the institutions’ portfolio, besides refining the institutional risk management approaches and mitigation measures.
11. Build staff capacities to operate in the new business environment in the post-pandemic world
Financial institutions may need to develop and disseminate content for their staff to prepare them better to work in the new business environment. The institutions may enhance employee awareness on preparedness to manage shocks that may have an impact on the business operations of their clients in the future.
12. Boost the skills and capacities of clients to help build resilience and nudge them to adopt digital products and alternative channels
Financial institutions may need to connect with the clients and ensure regular client engagement through a digital client management platform. The institutions may support individuals and enterprises to build skills and capacities through access to training modules. These modules may cover digital capability and financial education for individuals, and business skills for the entrepreneurs. Such skills and capacity building measures may encourage clients to adopt digital products and alternative channels.
With these measures, financial institutions may align business operations with user needs and utilize digitization to deliver client-centric solutions. Financial institutions will also be able to respond better to the economic disruption and make a faster recovery within the current social and economic situation. Thus, they will be able to support businesses, much like Philip, whom we met in the first blog, as he rebuilds his livelihood. If financial institutions revive and re-engineer, they can offer some hope for people like Philip and their enterprises.
Written by

Anup Singh
Associate Director
Leave comments