Covered! How informal youth workers in the gig economy can be insured
by Peter Charagu
May 22, 2020
5 min
In this blog, we highlight how MSC uses its behavioral and human-centered research to understand the dynamic nature of work for the youth, especially those in the informal sector, risks that affect them, and their everyday use-cases to design effective microinsurance product concepts for gig platforms and workers.
Technology has the potential to increase employment rates amongst youth, especially in informal work. In 2019, a report on Gig Economy estimated the size of the gig economy (access to work online) in Kenya at USD 109 million, employing over 36,000 workers. The report further states that based on the current investment the gig economy is witnessing, the sector is projected to grow by 32% in the next five years, to a value of USD 345 million and will employ over 93,000 workers. The informal sector in Kenya has consistently represented over 80% of the workforce. The use of technology provides a significant opportunity to offer jobs and employment to the informal sector.
The current COVID-19 pandemic has just outlined how vulnerable job and social security is for gig workers. CGAP reports that most workers on platforms, offering artisanal and personal services, are seeing up to 90% reduction of business for them. Most have had to dig into their savings, if any, to take care of their living expenses. Those without savings are finding it hard to cope with the lockdowns. Gig work also does not fall within the customary contractual structures and grievance mechanisms provided by traditional formal employment. Insurance, as an example, has traditionally targeted the formal sector. There are very few insurance companies that offer adequate and accessible products to gig workers. The nature of gig work makes offering insurance products to the gig workers much more difficult. Gig work varies significantly based on the technical platform, type of work, and risk exposure. Online gig workers are, in particular, more complicated to insure due to the on-demand and unpredictable nature of gig work.
Several gig platforms such as Lynk based in Kenya provide professional services through matching customers to a pool of blue-collar workers. Lynk has a focus on generating employment opportunities for youth and is on track to achieve this with over 60% of its workers in the youth category. A large portion of their workforce, however, have inadequate access to insurance. Through support from the Mastercard Foundation, MSC supported the development and delivery of microinsurance products to serve gig workers. In our previous blog, we defined the platform economy and explored the challenges faced by gig workers. Poor and irregular pay, unstructured contracts or lack thereof, and unpredictable cash flows are some of the leading reasons that make gig workers a segment that is an ill fit for traditional insurance companies.
Mutiso, a carpenter who lacked health assistance when he needed
Mutiso is a twenty-eight-year-old carpenter, who runs a furniture workshop on one of the busy roadsides in Nairobi. He joined Lynk as a pro, three years ago, upon recommendation from a friend. As his regular business had issues of seasonality, he envisaged that these gigs on the platform would lead him to regular customers and smoothen his cash flow.
Mutiso has been very careful with his work that involves dangerous tools to cut, shape, and build furniture. He rarely had an accident at work. However, two years ago, as he was sawing a large trunk of wood to make a table, he moved the log too fast, and the saw got to his hand. He cut half-way through his forearm. This injury put him out of work for six months. He had no source of income during the period and no health insurance. It cost him over KES 200,000 (USD 2,000) just for the hospital bill, and he had to rely on friends and family to be able to pay for his treatment.
How can we create microinsurance product concepts for gig workers and platforms?
Behavioral research and human-centered design can be applied to develop product concepts that are adequate, accessible, and meet the needs of the gig workers. Our research shows that most gig workers have no access to formal insurance, although they recognize and experience several risks. Also, our assessment shows that most traditional products provided by insurance companies are not adequate to serve the unique needs of the gig workers’ segment.
The core use cases of insurance for young gig worker included the following:
Developing microinsurance product concepts for gig workers
Based on our research, key insights to develop microinsurance product concepts for gig workers include:
- The flexibility of the worker’s gigs: Gig workers would like to be able to afford a cover before they commence their gigs. Thus, the product should have an on-demand cover that the gig workers may pay for when carrying out gigs.
- Incorporate the use of technology: Considering the tech-savvy nature of the youth gig workers and need for an efficient experience, providers must digitize and embed technology at each stage of service. Thus, the core processes such as enrollment, premium payment, and claim settlement should be digitized.
- Affordable and dynamic pricing: Differential pricing and payment models could make it easier for the gig worker to afford the premiums. To reduce the cost of access to insurance, a liability sharing model where both the gig platform and the gig workers contribute towards the premium payment. The flexibility of gigs demands a dynamic pricing model where the gig workers may split and pay premium across the predicted number of gigs.
Developing a microinsurance model that works for gig workers
Based on our research, an insurance provider is piloting an umbrella personal accident product for the gig economy, to include the following attributes:
- On-demand access: Together with the platform, the provider has assessed the overall platform’s insurance needs to develop and deliver an umbrella Personal Accident (PA) cover for all the gig workers associated with the platform. The cover is applicable during the working period and protects gig workers against all the risks associated with the gigs. The provider is offering work injury benefits to all the gig workers in line with existing labor regulations.
- Pooled and agnostic: The pooled insurance product covers a specific and pre-determined number of workers at any given point of time. The number depends on the history of active daily workers on the platform but does not prescribe the specific individuals. This approach acknowledges that from the pool of the gig workers, not all of them will work on the same day or at the same time, and it is certain that not all workers are at risk every day. If only 400 out of 1,000 workers are active every day, the platform pre-pays insurance for only the daily active workers. Consequently, the premium paid per worker is significantly reduced.
Through behavioral and human-centered research, a provider may understand the dynamic nature of work, risks that affect them, and practical use cases, and may design effective microinsurance product concepts for gig platforms and workers. The COVID-19 pandemic has brought to life the reality that informal workers unjustifiably get the short end of the stick concerning financial services and specifically insurance. Regardless of informal workers’ equitable and unappreciated contribution to the economy and society, our embrace of technology in the gig economy can indeed extend the benefits enjoyed by formal economy workers to the informal workers.
The abridged version of this blog was first released on NextBillion.
 by
by  May 22, 2020
May 22, 2020 5 min
5 min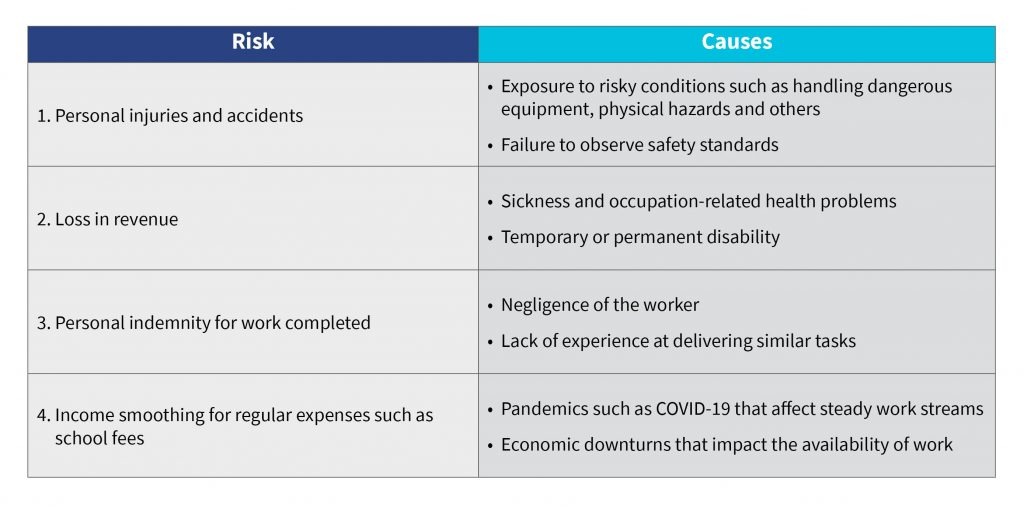

Leave comments